×
Drug Overdose Deaths in the United States
BASE MAP
Causes of Death
STATES
| 21.8 |
Example Text
|
| 26.6 | Prosperity Index Score |
| 26.6 |
Hover over a variable in the data table, and its definition will appear below
| 31 |
| Total Deaths |
| 39,434 |
| Population |
| Rural |
| Urban / Rural |
| Mortality Type | Year | County Name | State Name | United States |
| Drug Overdose Mortality | 2018-2021 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2014-2017 | ||||
| 2010-2013 | ||||
| Opioid Overdose Mortality | 2018-2021 | |||
| 2014-2017 | ||||
| 2010-2013 |
| Component | Score | Sub-Component | State Average | United States | |
| Economic - Risk | 5 | Poverty Rate | |||
| Number of Industry Dependencies | |||||
| Net Migration per 100 people | |||||
| Labor Force Participation Rate | |||||
| Economic - Resilience | 5 | Self-employment Rate | |||
| Business Establishments per 100 workers | |||||
| Number of Hospitals Beds per 10,000 population | |||||
| Median Household Income | |||||
| Social - Risk | 5 | Digital Distress (1= Low Distress, 2 = Medium Distress, 3 = High Distress) | |||
| High School Drop Out Rate | |||||
| Teen Birth Rate per 1,000 population | |||||
| All-cause Mortality Rate per 100,000 population | |||||
| Social - Resilience | 5 | 501 c3 and c4s per 10,000 population | |||
| Educational Attainment - Bachelor's Degree or more | |||||
| Primary Care Providers per 10,000 population | |||||
| Voter Participation Rate |
The prosperity index was developed with support from a Technical Expert Panel (TEP) convened by Betty-Ann Bryce, while detailed to the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy as Special Advisor for Rural Affairs from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Rural Development agency. TEP members represented a diverse group of stakeholders with a wide range of expertise. The TEP included: Anita Chandra (RAND Corporation), Courtney Cuthbertson (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign), Alison Davis (University of Kentucky), Marjory Givens (Wisconsin Public Health Institute; County Health Rankings), Shannon Monnat (Syracuse University), Robert Pack (East Tennessee State University), Laura Palombi (University of Minnesota), Khary Rigg (University of South Florida), David Terrell (Indiana Communities Institute, Paul State University) Brian Smedley (National Collaborative for Health Equity), and Sarah Willen (University of Connecticut).
The prosperity index provides a single numerical measure designed to reflect the prosperity of a county. For the overall prosperity index score, 1 represents most prosperous counties and 5 represents least prosperous counties. For the component scores, 1 represents lowest risk or highest resilience and a score of 5 represents highest risk or lowest resilience.
The prosperity index is calculated for each county in the United States using standardized values of 16 indicators belonging to one of four component classes associated with prosperity. The four components represented are Economic Risk, Economic Resilience, Social Risk, and Social Resilience. Each of these four components is comprised of four indicators reflecting aspects of that dimension that are aggregated to create the component score.
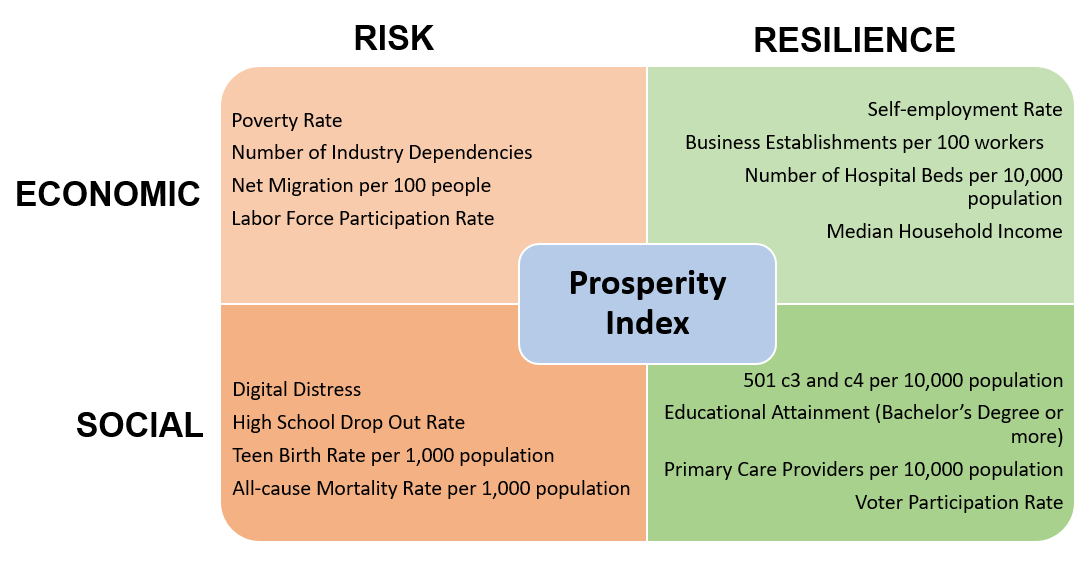
The economic dimensions, risk and resilience, provide two numerical measures for the degree to which a county is economically vulnerable to, or protected from the effects of public health and well-being challenges and crises. The economic risk experienced by a county is qualified or mitigated by its level of economic resilience, the strength of its protective factors.
Similarly, social risk and social resilience both have a role in determining the vulnerability of a county. Taking both economic factors and societal factors into consideration gives the most complete picture of the county and can help users refine focus for initiatives that seek to improve quality of life by reducing risk and increasing resilience.
The index may provide benefit to public health officials in counties where a certain level of vulnerability may exist even though a crisis has not yet been experienced. Proactive exploration of the index and digging deeper into the factors that it highlights will allow end users to reduce the likelihood or severity of these crises.
Indicators were selected based on several criteria, including the ability to influence the indicator at the local level, the availability of county-level data that is consistently reported and publically available, and data that could be considered indicators of community-level prosperity. Indicators that were suggested but ultimately not included in the prosperity index due to data limitations or challenges are: access to transportation, income inequality, and access to early childhood education.
| Component | Indicator | Data Source | Calculation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic – Risk | Poverty Rate | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2014-2019) | Percentage of individuals below poverty |
| Number of Industry Dependencies | USDA Economic Research Service (2015) | Total number of industry-dependencies calculated from binary indicators for industry-dependence (mining, farming, manufacturing, recreation) | |
| Net Migration per 100 people | Census Population Totals and Components of Change (2020-2022) | Net migration rate was calculated by pulling the total net migration (domestic and international) between July 1st 2021 and July 1st 2022, then dividing it by the population of the county on July 1st 2021.. | |
| Labor Force Participation Rate | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2017-2021) | Among the civilian non-institutionalized population aged 25 to 54, the percentage that is working or actively looking for work | |
| Economic – Resilience | Self-employment Rate | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2017-2021) | Percentage of total workforce self-employed in own incorporated business |
| Business Establishments per 100 workers | U.S. Census - County Business Patterns (2018) | Number distinct business establishments per workers 16 years and older | |
| Number of Hospital Beds per 10,000 population | HRSA Area Health Resources Files (2019-2020) | Number of hospital beds per 10,000 population | |
| Median Household Income | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2017-2021) | Median household income in the past 12 months (in 2017 inflation-adjusted dollars) | |
| Social – Risks | Digital Distress | Purdue Center for Regional Development: Digital Distress Indicator (2017-2021) |
|
| High School Drop Out Rate | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2017-2021) | Percentage of persons aged 16 to 19 years who neither graduated from, nor are currently enrolled in, high school | |
| Teen Birth Rate per 1,000 population | CDC NCHS (2018) | Estimated teen birth rates for females aged 15 to 19 years per 1,000 | |
| All-cause Mortality Rate per 100,000 population* | CDC NCHS NVSS – Multiple cause of death data (2019) | Number of deaths of all causes per 100,000 population (age-adjusted) | |
| Social – Resilience | 501 c3 and c4s per 10,000 population | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) (2020) | Number of 501 c3 and c4 organizations per 10,000 population |
| Educational Attainment- Bachelor’s Degree or more | U.S. Census Bureau, ACS 5-year estimates (2017-2021) | Percentage of population 25 years and older with a Bachelor's, Master's, Professional, or Doctorate degree | |
| Primary Care Providers per 10,000 population | HRSA Area Health Resources Files (2019-2020) | Number of primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants per 10,000 population | |
| Voter Participation Rate^ | MIT Election Data and Science Lab (2018) | Percentage of eligible voters that voted in the 2016 presidential election |
*The all-cause mortality data did not have mortality rates for about 80 counties. For these counties the mortality subcomponent did not contribute a positive or negative result to the overall score (effectively a mean imputation).
^The voter turnout indicator was not readily available for Alaska since the raw data included voter totals by Congressional House District. A proportional allocation method based on population overlap was devised to estimate the voter turnout for each county (borough) in Alaska.
The prosperity index is calculated for each county in the United States using standardized values of 16 indicators belonging to one of four component classes associated with prosperity. The four components represented are Economic Risk, Economic Resilience, Social Risk, and Social Resilience. Each of these 4 components is comprised of 4 subcomponents reflecting aspects of that dimension that are aggregated to create the component score.
Each indicator, also known as a subcomponent, was scaled to have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. This is referred to as the standardized subcomponent value. Then a clustering algorithm grouped all of the counties into 5 homogenous groups according to the standardized values thus providing a score (1 through 5) for each county for each subcomponent.
At the component level, the 4 subcomponent standardized values within the component are summed to create a component value. The counties are then clustered according to the component value to create the component scores 1 through 5.
Finally the component values are summed for each county to create the prosperity value. The counties are then grouped into 5 classes with 1 representing the most prosperous and 5 representing the least prosperous. This 1-to-5 score is the final prosperity index score.
Click here to download a Microsoft Excel file containing the data used in the Overdose Mapping Tool.
The interactive tool was created in JavaScript using the Leaflet library. Data was processed using SAS and converted from shapefile to TopoJSON using the Mapshaper web client. Several data sources were accessed in the development of this tool (more information on the data sources used in the prosperity index can be found on the prosperity index tab):
The tool presents crude mortality rates for the population. The combined population estimates for the time period (either 2010-2013, 2014-2017 or 2018-2021) are the denominator for the mortality rates. Five-year average mortality rates were used for this tool in order to maximize the number of counties with a reliable crude mortality rate. For counties with fewer than 10 deaths over the five-year time period, the number of deaths is suppressed, and therefore a mortality rate is not provided. However, when possible, we have calculated the maximum crude mortality rate based on the population and the assumption of less than 10 deaths.
The table below describes each of the data sources and definitions for the variables included in the tool.
This website is funded through a grant from the Bureau of Justice Assistance, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice. Neither the U.S. Department of Justice nor any of its components operate, control, are responsible for, or necessarily endorse this website (including, without limitation, its content, technical infrastructure, and policies and any services or tools provided).
NORC at the University of Chicago conducts research and analysis that decision-makers trust. As a nonpartisan research organization and a pioneer in measuring and understanding the world, we have studied almost every aspect of the human experience and every major news event for more than eight decades. Today, we partner with government, corporate, and nonprofit clients around the world to provide the objectivity and expertise necessary to inform the critical decisions facing society.
For more information please contact:
Megan Heffernan, MPH
Senior Research Scientist, Public Health Research, NORC at the University of Chicago
heffernan-megan@norc.org | (301) 310-5089
Michael Meit, MA, MPH
Deputy Director, ETSU/NORC Rural Health Equity Research Center
Director of Research and Programs, ETSU Center for Rural Health Research
Senior Fellow, Public Health Research, NORC at the University of Chicago
meitmb@etsu.edu | (240) 273-2751
For more information on funding and other resources, visit the Rural Community Toolbox.
<iframe width="975" height="570" src="https://opioidmisusetool.norc.org/embed/map/map.html" frameborder="1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Embed table for Menifee County, KY in 2011 - 2015
<iframe width="975" height="630" src="https://opioidmisusetool.norc.org\embed\D\T2\table21165.html" frameborder="1" allowfullscreen> </iframe>
This tool allows researchers, policymakers, journalists, and the general public to create county-level maps illustrating the relationship between community and population demographics and fatal drug overdoses—including opioids—in the United States. Insights derived from this tool can be used to target resources and interventions, and inform media coverage related to overdose deaths in the U.S.
The user has the option to select the data to include as the base layer of the map. The options for the base layer include Drug Overdose or Opioid Overdose Mortality or the overall Prosperity Index or its sub-component scores. More detail on the Prosperity Index can be found on the “Prosperity Index” page. For the overdose mortality data, you can select the timeframe from the drop down on the top left of the map. The three options are: 2018-2021, 2014-2017, and 2010-2013. You can use the List of Counties to link directly to data on a particular county, or click on specific counties on the map.
Click on the ”timeframe” drop down on the upper-left section of the screen to change the years represented for the drug overdose and socio-demographic and economic data.
To view state-level data, click the "state/county" drop down in the upper-right section of the screen and select "State".
Use the “urban/rural” drop down to compare data from rural and urban counties.
Choose variables from the left-hand column to layer county-level economic and demographic data on top of the baseline drug overdose mortality data. By showing the variables as translucent circles of varying sizes, the tool allows users to clearly see how a given measure relates to the baseline drug overdose mortality rate. For example, choosing “Poverty Rate” will demonstrate the relationship between an individual county’s poverty rate and its overdose mortality rate. Additionally, behavioral health resources, such as mental health and substance use facilities per capita, can be added as an overlap to the map.
When second-layer data has been added onto a base map, users can select “Open Correlation Graph” to see a graph that shows the correlation between the two indicators, including the correlation coefficient. Correlation coefficients are typically used to evaluate the association between two variables. These coefficients range from -1 to +1 and represent the strength of the relationship between the two variables. Values of 0 indicate no meaningful associations between the two variables. As the correlation values approach either end (-1 or +1) of the range, the association becomes stronger, where values closer to 0 indicate weaker relationships. Negative values (those less than 0) indicate decreasing or inverse relationships (as one variable increases, the other decreases), and positive values (greater than 0) demonstrate increasing relationships (as one variable increases, the other also increases). The two types of correlation coefficients used for this tool include Pearson’s correlation coefficient and Spearman’s correlation coefficient. Pearson’s correlation coefficient is used here when examining two continuous variables (numerical in scale). Spearman’s correlation coefficient is used when at least one of the variables (or possibly both) are not continuous (i.e., categorical or ordinal in nature). Pearson’s correlation coefficient is specific to evaluating the linear association between the two continuous variables, while Spearman’s correlation coefficient does not require a linear relationship, merely an increasing (or decreasing) association between the variables.
On the left hand side of the screen, there is a drop down for “Add Map Overlay.” Available map overlays include: geolocations of Native American Reservations; outline of persistent poverty counties; location of major highways; and outlines of federally defined regions.
For each county, there are three fact sheets, which can be found by clicking on “View Details” when selecting a county. The fact sheets include: 1) Drug Overdose Mortality data; 2) Prosperity Index data; 3) Socio-Demographic data; 4) Economic data; and 5) Behavioral Health Resources data. For all data tables, county, state, and national data are provided, to provide benchmarks for counties. The name and location of substance use and mental health facilities are also provided in the drop down menus at the bottom of the fact sheet.
The Recovery Ecosystem Index (REI) was developed with support from a Technical Expert Panel (TEP) convened by the ETSU/NORC Rural Health Equity Research Center (RHERC) and Fletcher Group, Inc. TEP members represented a diverse group of stakeholders with a wide range of expertise. The TEP included: Dr. Robert Ashford (Unity Recovery), Matt Boggs (Ryker Douglas), Dr. Anita Chandra (RAND Corporation), Dr. Kimberly Dash (Education Development Center), John Gale (University of Southern Maine, Cutler Institute), Peter Gaumond (Office of National Drug Control Policy), Carolyn Hardin (National Association of Drug Court Professionals), Christopher Hart (Unity Recovery), Sierra Helfrich (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), Patrick Hibbard (JEAP Training Institute at Oregon Social Learning Institute), Pam Johnson (FAHE), Dr. John Kelly (Harvard Medical School, Recovery Research Institute), Dr. Ron Manderscheid (National Association for Rural Mental Health, National Association of County Behavioral Health and Developmental Disability Directors), and Robin Phillips (National Rural Transit Assistance Program).
The Recovery Ecosystem Index provides a single numerical measure designed to reflect the strength of the recovery ecosystem of a county. For the overall Recovery Ecosystem Index score, 1 represents the strongest and 5 represents the weakest recovery ecosystem.
The index was designed to measure the strength of rural county-level recovery ecosystems, and provide data to support community planning, programming and technical assistance designed to strengthen recovery ecosystems throughout the rural United States. The index is broken down into three components that impact the strength of a recovery ecosystem: Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Treatment; Continuum of SUD Support; and Infrastructure and Social.
The SUD Treatment component includes the number of substance use treatment facilities per capita, number of providers licensed to administer buprenorphine per capita, average distance to nearest medication-assisted treatment (MAT) provider, and the number of mental health providers per capita.
The Continuum of SUD Support component includes the number of recovery residences per capita, average distance to nearest syringe-service program (SSP), number of Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or Self-Management and Recovery Training (SMART) meetings per Capita, drug court presence, Drug-Free Communities Coalition grant presence, and policy environment score.
The Infrastructure and Social component includes vehicle availability, severe housing cost burden, broadband access, and social associations per capita.
To select the indicators, we first conducted a literature review to determine the key components of a recovery ecosystem. We developed a list of all potential indicators based on this review and input from the TEP. We then prioritized a list of indicators based on TEP feedback, and ultimately included the following list of indicators. In order to be selected, the indicator had to have publicly available data for all counties in the U.S.
| Component | Indicator | Data Source | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUD Treatment | Number of Substance Use Treatment Facilities Per Capita |
SAMHSA (N-SSATS Data) (As of February 2022) |
Number of substance use treatment facilities per 100,000 residents |
| Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Treatment score | See Recovery Ecosystem Index page | Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Treatment score | |
| Continuum of SUD Support score | See Recovery Ecosystem Index page | Continuum of SUD Support score | |
| Infrastructure and Social Factors score | See Recovery Ecosystem Index page | Infrastrucutre and Social Factors score |